
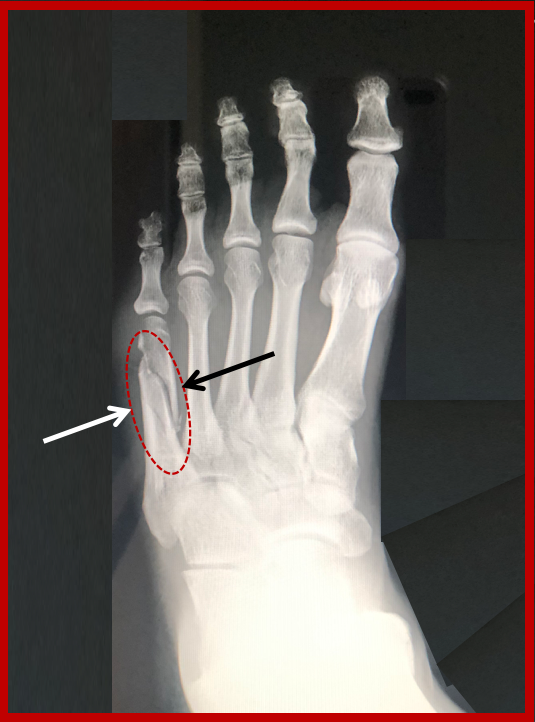
Plain film – anterior-posterior, oblique and lateral viewsĬT is seldom necessary. What radiological investigations should be ordered?Ĭhildren with pain, swelling and/or deformity to forefoot require foot radiographs. The forefoot will usually appear swollen with bruising, and the patient may be unwilling or unable to bear weight.

Occasionally, this is part of a LisFranc injury (tarso-metatarsal fracture-dislocation) 4.
Stress from heavy / repetitive intensive trainingįractures of the 2nd, 3rd and 4th metatarsals rarely occur in isolation and commonly result in fracture/s of the adjacent metatarsals. Crush injury caused by a heavy object falling onto the foot or motor vehicle tyre running over foot. How common are they and how do they occur?įractures of the metatarsals are common injuries in children.Ĭhildren 5 year or younger are more likely to fracture 1st metatarsal, whereas children older than 5yrs are more likely to injure 5th metatarsal Growth plate involvement (Salter Harris Classification)ģ. Location of fracture (base, middle, proximal metatarsal). Metatarsal fracture are classified by the following: Early surgical fixation reduces time to healing and time to return to sports.Metatarsal fractures are common in the paediatric population and rarely require operative management.Ĭare should be taken in differentiating an avulsion fracture of the fifth metatarsal from a Jones fracture, due to the risk of nonunion in the latter. Nondisplaced avulsion fractures of the fifth metatarsal tuberosity require symptomatic therapy only (elastic or soft bandage followed by firm shoe when tolerated).įractures of the proximal fifth metatarsal diaphysis require more aggressive treatment, such as early surgical fixation or prolonged casting with no weight bearing. Stress fractures of the metatarsal shaft usually heal well without immobilization and typically respond well to cessation of the causative activity for four to eight weeks. Most nondisplaced metatarsal shaft fractures require only a soft elastic dressing or firm, supportive shoe and progressive weight bearing. If there is more than 3 to 4 mm displacement in a dorsal or plantar direction, or if dorsal/plantar angulation exceeds 10 degrees, reduction is usually required. If radiography reveals a normal position seven to 10 days after injury, progressive weight bearing may be started, and the cast may be removed three to four weeks later.įractures of a single metatarsal with lateral or medial displacement usually heal well without correction and may be managed like nondisplaced fractures. Nondisplaced fractures of the proximal portion of metatarsals 1 through 4 can be managed acutely with a posterior splint followed by a molded, non–weight-bearing, short leg cast. Treatment of fractures distal to the tuberosity should be individualized based on the characteristics of the fracture and patient preference. Radiographs should be carefully examined to distinguish these fractures from tuberosity fractures. Proximal fifth metatarsal fractures that are distal to the tuberosity have a poorer prognosis. Avulsion fractures of the proximal fifth metatarsal tuberosity can usually be managed with a soft dressing. Stress fractures of the first to fourth metatarsal shafts typically heal well with rest alone and usually do not require immobilization. Nondisplaced fractures of the metatarsal shaft usually require only a soft dressing followed by a firm, supportive shoe and progressive weight bearing. Injuries to this ligament require referral or specific treatment based on severity. 
If the midfoot is injured, care should be taken to evaluate the Lisfranc ligament. Referral is generally indicated for intra-articular or displaced metatarsal fractures, as well as most fractures that involve the first metatarsal or multiple metatarsals. The fracture should then be characterized and treatment initiated. Initial evaluation should focus on identifying any conditions that require emergent referral, such as neurovascular compromise and open fractures. Patients with metatarsal fractures often present to primary care settings.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
